In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assay (IVBA) Sampling Guidance Update - Part 4 Soil Sampling Best Practices and Laboratory Methods to Measure IVBA & RBA
Archived: Monday, April 1, 2024
Sponsored by: U.S. EPA Bioavailability Technical Review Workgroup (BAC)
The Technical Review Workgroup (TRW) Bioavailability Committee recently published the "Guidance for Sample Collection for In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assay for Arsenic and Lead in Soil and Applications of Relative Bioavailability Data in Human Health Risk Assessment." This is an update to the 2015 Guidance for Sample Collection for In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assay for Lead (Pb) in Soil. The update is intended to help EPA risk assessors, remedial project managers, and on-scene coordinators develop and use bioavailability data at their sites. It incorporates sample planning and data analysis recommendations from EPA's Guidance on Systematic Planning Using the Data Quality Objectives Process that are pertinent to sampling for In Vitro Bioaccessibility (IVBA) and Relative Bioavailability (RBA). It also clarifies the application of IVBA and RBA data to human health risk assessment, the development of risk-based goals at CERCLA remedial and removal sites and includes arsenic (As) which was recently added to the In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assay.
The TRW has developed a series of trainings based on the updated guidance. This session will focus on a discussion of soil sample collection and processing best practices and methods to directly measure relative bioavailability (RBA) or estimate RBA by measuring in vitro bioaccessibility via EPA Method 1340 at soil arsenic and lead contaminated sites. This training will target a general audience of regional staff working in risk assessment, remediation, emergency response, technical support, and quality assurance. The training will be an approximately one hour long and will include time for general discussion. Members of the Bioavailability Committee and a Regional representative will be present to answer questions in real time.
 Clay Nelson, BioGeoChem Scientific, LLC (claymnelson@gmail.com)
Clay Nelson, BioGeoChem Scientific, LLC (claymnelson@gmail.com)
Clay Nelson is the principal of BioGeoChem Scientific LLC, an environmental consulting firm based in Austin, Texas. Clay brings 18 years of experience in inorganic analytical chemistry, statistical data analysis, and risk assessment, with a focus on toxic metal(loid) exposure and metal bioavailability/bioaccessibility . Clay has co-authored over 25 articles in the peer-reviewed literature on topics ranging from the development and validation of in vivo and in vitro methods to measure lead and arsenic bioavailability/bioaccessibility, to development of soil metal remediation technologies, to assessment of lead and other metal(loid)s in drinking water and house dust. Clay is currently leading the development of a statistical simulation tool to estimate decision confidence in the assessment of lead and arsenic contaminated soils to inform sample planning and data quality objective assessment.
Sydney Chan, U.S. EPA - Panelist
Karen Bradham, U.S. EPA - Panelist
Matthew Lambert, U.S. EPA - Panelist
Gary Diamond, SRC - Panelist
Julie Klotzbach, SRC - Panelist
Ghassan Khoury, U.S. EPA - Panelist
Charles Partridge, U.S. EPA - Panelist
Moderator:
 Jean Balent, U.S. EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division (balent.jean@epa.gov or 202-566-0832)
Jean Balent, U.S. EPA Technology Innovation and Field Services Division (balent.jean@epa.gov or 202-566-0832)
Ms Balent is on the staff of the EPA's Technology Innovation and Field Services Division where she has worked to collect and disseminate hazardous waste remediation and characterization information since 2003. Ms Balent manages the Clean Up Information Network website and actively supports online communication and collaboration resources available to EPA. She formerly worked with the US Army Corps of Engineers Environmental Engineering Division in the Buffalo District. Ms Balent was also a member of the SUNY-Buffalo Groundwater Research Group where she constructed and tested large scale models of groundwater flow. Ms Balent has also conducted research relating to the Great Lakes, environmental remediation, and brownfields re-development. She holds a Bachelor's degree in environmental engineering from SUNY-Buffalo and a Master's degree in Information Technology from AIU.
Webinar Slides and References:
Additional Resources:
- Soil Bioavailability at Superfund Sites: Technical Assistance
 Guidance for Sample Collection
Guidance for Sample Collection- TRW BAC email (bahelp@epa.gov)
- TRW BAC website
- EPA Reports:
- Guidance on Choosing a Sampling Design for Environmental Data Collection (2002)
 Guidance for Sample Collection for In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assay for Lead in Soil and Applications of Relative Bioavailability Data in Human Health Risk Assessment (2021)
Guidance for Sample Collection for In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assay for Lead in Soil and Applications of Relative Bioavailability Data in Human Health Risk Assessment (2021) SW-846 Test Method 6200: Field Portable X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry for the Determination of Elemental Concentrations in Soil and Sediment (2007)
SW-846 Test Method 6200: Field Portable X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry for the Determination of Elemental Concentrations in Soil and Sediment (2007) Superfund & Emergency Management X-Ray Fluorescence Field Operations Guide (2022)
Superfund & Emergency Management X-Ray Fluorescence Field Operations Guide (2022) SW-846 Compendium: Chapter 3, Inorganic Analytes
SW-846 Compendium: Chapter 3, Inorganic Analytes Standard Operating Procedure for an In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assay for Lead and Arsenic in Soil, April 20, 2017
Standard Operating Procedure for an In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assay for Lead and Arsenic in Soil, April 20, 2017 USDA. Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service. Federal Domestic Soil Quarantines
USDA. Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service. Federal Domestic Soil Quarantines- Referenced Peer-Reviewed Studies:
- Bradham et al. (2013). Mouse assay for determination of arsenic bioavailability in contaminated soils.
- Bradham et al. (2018). Comparison of mouse and swine bioassays for determination of soil arsenic relative bioavailability.
- Li et al. (2016). Arsenic relative bioavailability in contaminated soils: Comparison of animal models, dosing schemes, and biological endpoints.
- Bradham et al. (2016). Estimating relative bioavailability of soil lead in the mouse.
- Scheckel et al. (2013). Amending soils with phosphate as means to mitigate soil lead hazard: a critical review of the state of the science.
Help & FAQs
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Content Questions?
Call Sydney Chan at 303-241-9767 or chan.sydney@epa.gov - Technical Problems?
Leave us a comment - Cancel Your Registration
- My Participation Records
- CEU Credits and PDHs
Zoom Resources
Before Webinar Day
This seminar will be delivered through Zoom. Participants are encouraged to update to the latest version of the Zoom application for the best experience.
If you are unable to install the Zoom application, most functions will be available if you join just using a modern web browser such as Chrome, Edge or Firefox. We strongly encourage you to run the Zoom Meeting Test prior to attending this webinar. Technical support on the day of the webinar will be very limited and subject to significant delays.
Backup Conference Call
If you cannot participate using online audio, you may join the optional call in line. After checking in for the live event using the instructions listed below, you will see several options to participate. Please click the links in option 4 to follow along by phone and obtain the call in number. If you cannot access the phone number, you may request the call in line from the event moderator in the Q&A or send an email to Jean Balent at balent.jean@epa.gov
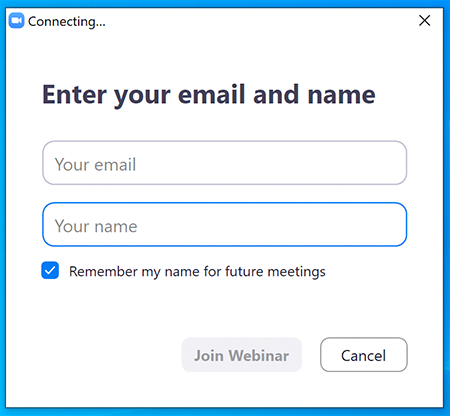
Click on "Join Webinar" at the top of this screen, enter your exact first and last name as you registered and enter the number of people attending at your location (including yourself). You should then be taken to the Zoom meeting room. Join with Zoom Application: For those joining with the Zoom application, you may be prompted to sign with a zoom account or join as a guest without signing in.
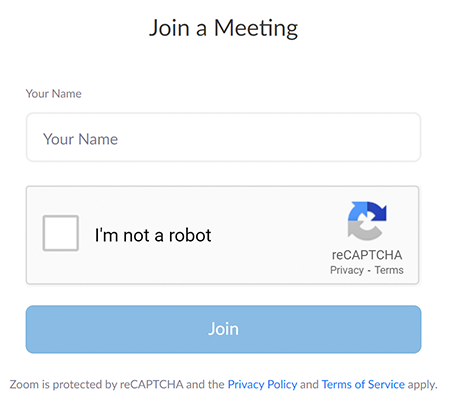
If joining as a guest, you will be prompted to enter your name and email address. Remember your name, image, video or voice may be visible to others in the live event. When done, click "Join" When it is time for the live event to start, the meeting host will admit you to the live Zoom meeting. Join via web browser (without the Zoom Application): For those joining with a web browser, you may close any pop ups prompting you to download the Zoom app. The next window will allow you to enter your name (first name and last name) and check the box that you are not a robot. Click the blue join button. You may also be asked to provide your email address before joining the room. Remember your name, image, video or voice may be visible to others in the live event. When done, click "Join" When it is time for the live event to start, the meeting host will admit you to the live Zoom meeting. You may need to periodically refresh the browser window to confirm if the host has admitted you. The presenters will control what slide you are viewing. You may submit questions online for the instructors to answer during the webinar by typing in the "Q&A" area. It is not necessary to wait until the question and answer periods to submit questions. At the end of the webinar you will be guided to our feedback form and links to additional resources, including the complete presentation. These links will remain active after the webinar. Provided for your convenience. Importing or accepting the invitation within this iCalendar file is not required, and declining the invitation does not cancel your registration. For additional information on iCalendar, please see our
iCalendar Help It is EPA's policy to make reasonable accommodation to persons with disabilities wishing to participate in the agency's programs and activities, pursuant to the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, 29 U.S.C. 791. Any request for accommodation should be made to Sydney Chan at 303-241-9767 or chan.sydney@epa.gov, preferably one week or more in advance of the webinar, so that EPA will have sufficient time to process the request. EPA would welcome specific recommendations from requestors specifying the nature or type of accommodation needed. EPA welcomes specific recommendations from requestors specifying the nature or type of accommodation needed. Please note that CLU-IN provides both alternate phone call-in options and closed captioning for all webinars, and requests for these specific accommodations are not necessary.
Webinar Day, Checking In

Moving Through Slides
Feedback & Links to Additional Resources
iCalendar File
Rehabilitation Act Notice for Reasonable Accommodation
Rehabilitation Act Notice for Reasonable Accommodation
It is EPA's policy to make reasonable accommodation to persons with disabilities wishing to participate in the agency's programs and activities, pursuant to the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, 29 U.S.C. 791. Any request for accommodation should be made to Sydney Chan at 303-241-9767 or chan.sydney@epa.gov, preferably one week or more in advance of the webinar, so that EPA will have sufficient time to process the request. EPA would welcome specific recommendations from requestors specifying the nature or type of accommodation needed. EPA welcomes specific recommendations from requestors specifying the nature or type of accommodation needed. Please note that CLU-IN provides both alternate phone call-in options and closed captioning for all webinars, and requests for these specific accommodations are not necessary.
Webinar Recording
By participating in this CLU-IN webinar, you automatically agree to authorize recording of audio and visual content presented during this live event and consent to subsequent use of this recording in the public domain by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. This recording may include questions, comments and poll responses provided by you during the live event in addition to your name, voice, image or likeness. This recording will be made available after the conclusion of the live event as part of the CLU-IN webinar archives, and will remain available indefinitely. If you do not wish to consent to the recording, please do not join the live event, and contact Jean Balent at 202-566-0832 or balent.jean@epa.gov to discuss your concerns.
Content Disclaimer
This webinar is intended solely to provide information to the public. The views and opinions expressed as part of this webinar do not necessarily state or reflect those of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. It is not intended, nor can it be relied upon, to create any rights enforceable by any party in litigation with the United States, or to endorse the use of products or services provided by specific vendors. With respect to this webinar, neither the United States Government nor any of their employees, makes any warranty, express or implied, including the warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, or assumes any legal liability or responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, apparatus, product, or process disclosed, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights.