Overview
Optimization Stages: Design
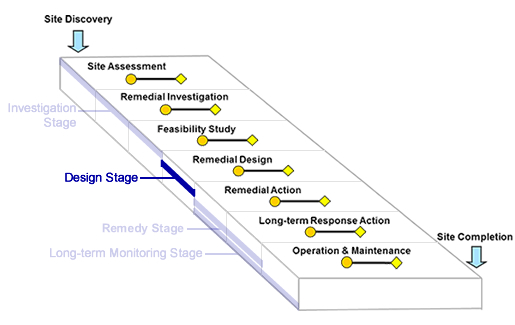
Optimization during pre-design, design or redesign evaluates the selected remedy prior to implementation and operation. It considers the goals of the remedy, conceptual site model (CSM), available site data, performance considerations, protectiveness, cost-effectiveness and closure strategy. Design stage optimization may add greater certainty to the selected remedy and ensure streamlined operations from the start of the project. To learn more about the related Superfund pipeline stage, visit Remedial Design  .
.
To see information about optimization for the other pipeline or optimization stages, visit Investigation stage, Remedy stage or LTMO stage.
Following are example types of data analyses performed during a design stage optimization.
- Analysis of investigation data
- Analysis of treatability and pilot study results
- Interpretation of the CSM and identification of data gaps
- Evaluation of design parameters developed by site team
- Estimation of pump and treat (P&T) extraction rates for plume capture
- Estimation of treatment chemical loading, available treatment technologies, and expected performance
- Estimation of oxidant or nutrient demand for in-situ remedies
- Estimated demand for soil/aquifer heating
- Estimates of other common remedy effectiveness and cost drivers
- Simplistic analytical or numerical modeling to assist with conceptual site model refinement
- Simplistic analytical or numerical modeling to assist with development of appropriate performance monitoring
- Identification of alternative remedy components
- Cost analysis of various technologies and approaches considered during design
- Consideration of green best management practices
- Preliminary green remediation environmental footprint analysis
Additional information on optimization is available within Superfund Remediation Optimization: Definition, Scope, and Approach. In addition, following are some of the resources used during an investigation stage optimization.
Selected Resources
Click on a column heading to sort the table. Search for additional publications or resources by keyword or topic using the Search page.




